If you are a coffee lover, you may be curious about the caffeine content in your favorite beverage. Caffeine is a natural stimulant found in many drinks and foods, including coffee, tea, energy drinks, and chocolate. It can have positive effects on your mood, alertness, and performance, but it can also cause negative effects if consumed in excess.
This blog will explore the caffeine content of coffee, including how much caffeine is in a typical cup, how much is too much, and which Starbucks drink has the most caffeine. We will also discuss the history and popularity of coffee and the factors that affect its caffeine content.
What is caffeine?
Caffeine is a naturally occurring stimulant that belongs to a group of compounds called xanthines. It works by blocking the action of adenosine, a neurotransmitter that promotes sleep and suppresses arousal.
By inhibiting adenosine, caffeine releases neurotransmitters like dopamine and norepinephrine, which can lead to increased alertness, mood, and cognitive performance.
Caffeine is found in various amounts in different foods and drinks, including coffee, tea, soda, energy drinks, and chocolate.
The amount of caffeine in a product depends on several factors, such as the type and quality of the source material, the processing method, and the serving size.
The history and popularity of coffee
Coffee is a popular beverage that has been enjoyed for centuries in many cultures around the world. Its origin can be traced back to the highlands of Ethiopia, where coffee trees grew naturally and were harvested for their beans.
From there, coffee spread to the Arabian Peninsula and beyond, becoming a global commodity in the 16th century.
Today, coffee is one of the most widely consumed beverages in the world, with millions of people starting their day with a cup of coffee. It is available in many forms, from hot brewed coffee to espresso shots, iced coffee, and flavored drinks. Coffee shops like Starbucks have become cultural icons, offering a wide range of coffee-based beverages with various levels of caffeine.
In the next sections, we will dive into the caffeine content of coffee and its effects on health and performance. We will also compare different coffee drinks and provide tips on how to enjoy coffee in moderation.
Caffeine Content in Coffee
How is caffeine measured?
Measuring caffeine in coffee can be quite difficult. The easiest way to do it is to rely on averages. According to the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), an eight-ounce cup of coffee contains between 80 to 100 milligrams of caffeine. However, this is just an estimate and not an exact representation of the caffeine content in your cup of coffee.
If you want a more precise measurement, you can send samples of your coffee to an analytical chemistry lab. However, this method can be quite costly and time-consuming, as you need to prepare multiple samples of your coffee brewed the same way.
If you want a rough idea of the caffeine content in your coffee, you can use a simple estimation method. Weigh the dry coffee in grams and multiply it by 0.008. This method will give you 80mg of caffeine for each 10g of dry coffee. However, weakly extracted coffee might yield less caffeine.
Caffeine content in a standard cup of coffee
On average, an eight-ounce cup of coffee contains between 80 to 100 milligrams of caffeine. However, the caffeine content can vary depending on the type of coffee, the brewing method, and the serving size.
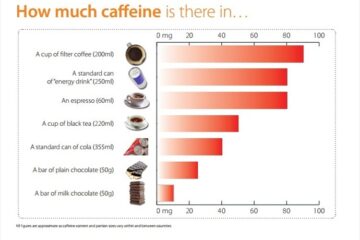
For example, a 12-ounce can of soda typically contains 30 to 40 mg of caffeine. This is significantly less than the amount of caffeine in a standard cup of coffee. Most major energy drinks contain between 70 and 100 mg of caffeine, which is also less than the caffeine content in coffee.
If you’re a fan of Starbucks, their venti beverage contains 24 ounces of coffee, which means you’ll be sipping up to 400 milligrams of caffeine. This amount can vary depending on the roast you choose, with their lightest roast potentially containing even more caffeine.
If you’re trying to cut back on your caffeine intake, decaf coffee might seem like a good option. However, don’t be fooled by the name – decaf coffee isn’t completely caffeine-free. According to the National Coffee Association, approximately 97% of caffeine is removed from the beans, meaning that an eight-ounce cup of decaf still contains about two milligrams of caffeine.
In conclusion, caffeine content in coffee can be difficult to measure accurately. While averages can give you a rough idea, the best way to determine the exact amount of caffeine in your coffee would be to send samples to an analytical chemistry lab.
Factors Affecting Caffeine Content
When it comes to caffeine content in coffee, there are several factors that affect it. Knowing these factors can help you determine how much caffeine you’re consuming.
Type of coffee beans
Different types of coffee beans contain varying levels of caffeine. For example, Robusta beans contain almost double the caffeine content of Arabica beans. This is why you may notice a difference in caffeine content when drinking different types of coffee.
Brewing method
The brewing method also affects the caffeine content in coffee. Brewed coffee, for instance, generally has a higher caffeine content than instant coffee. This is because brewed coffee involves steeping coffee grounds in hot water, allowing for more caffeine extraction compared to instant coffee.
Serving size
The serving size of your coffee also plays a role in the caffeine content. A standard eight-ounce cup of coffee typically contains between 80 to 100 milligrams of caffeine. However, larger serving sizes will have more caffeine content, so be mindful of the size of your coffee.
Other factors that affect caffeine content include the amount of coffee grounds used and how long the coffee is brewed for. If you’re looking to reduce your caffeine intake, consider using less coffee grounds or brewing for a shorter period of time.
It’s important to note that while coffee can be part of a healthy diet, too much caffeine can be unsafe. The recommended daily intake of caffeine is about 400 milligrams for healthy adults, which is roughly equivalent to four cups of coffee. Consuming more than this can lead to negative side effects such as headaches, difficulty sleeping, gastrointestinal issues, and jitteriness.
In addition to coffee, other sources of caffeine include energy drinks, soft drinks, chocolate, and some pain-relieving medications. It’s important to keep track of your overall caffeine intake, regardless of the source.
In conclusion, caffeine content in coffee is affected by various factors such as the type of beans, brewing method, and serving size. By understanding these factors, you can better determine how much caffeine you’re consuming and make adjustments as needed. Remember to consume caffeine in moderation and be mindful of your overall intake from all sources.
High Caffeine Coffees and Their Effects
If you’re a coffee lover, you might prefer brews with higher caffeine content. However, too much caffeine can lead to various side effects, including anxiety, restlessness, and jitters. In this article, we’ll discuss some of the high caffeine coffees and their effects.
Espresso
Espresso is a rich, concentrated coffee, and it’s a favorite choice for many caffeine lovers. An ounce of espresso contains approximately 63 milligrams of caffeine. However, espresso shots are typically 1.5 to 2 ounces, meaning a single shot could contain anywhere from 95 to 126 milligrams of caffeine.
Some people enjoy consuming multiple shots of espresso per day, but it’s important to be aware of your caffeine intake. Too much caffeine can cause heart palpitations, headaches, and insomnia.
Cold brew
Cold brew coffee is becoming increasingly popular, especially during the summer months. Cold brew coffee is prepared by steeping coffee grounds in cold water for an extended period. As a result, cold brew coffee has a smoother, less acidic flavor than regular coffee.
However, cold brew coffee also has a higher caffeine content, with an average of 200 milligrams per 12-ounce cup. That’s double the caffeine content found in a regular cup of coffee. The caffeine content also increases with brewing time, so be careful when consuming cold brew coffee.
Turkish coffee
Turkish coffee is a traditional unfiltered coffee that originated in Turkey. It is typically served hot, and it contains a high amount of caffeine per serving. A single cup of Turkish coffee can contain up to 165 milligrams of caffeine, which is almost twice as much caffeine as a regular cup of coffee.
While some people love the taste of Turkish coffee, it’s important to be aware of its high caffeine content. Too much caffeine can lead to nervousness, nausea, and even cardiac arrest.
In conclusion, high caffeine coffees can be enjoyable, but it’s important to be aware of the potential side effects of consuming too much caffeine. If you’re sensitive to caffeine or have underlying health conditions, it’s best to stick to lower caffeine brews and consume coffee in moderation. Always consult with your doctor if you have any questions or concerns about caffeine consumption.
Low Caffeine Coffees and Their Effects
If you’re looking for coffee options with less caffeine, there are several alternatives available. Whether you want to avoid caffeine or limit your intake, these low caffeine options can be a great choice for coffee lovers.
Decaf coffee
Decaf coffee is a popular choice for people who want to limit their caffeine intake but still enjoy the taste of coffee. Decaffeinated coffee is made by removing caffeine from coffee beans, either through a chemical or water process. On average, a cup of decaf coffee contains only 2 to 5 milligrams of caffeine, compared to 95 milligrams in a regular cup.
While decaf coffee still contains some caffeine, the amount is minimal. However, it’s important to note that decaf coffee has slightly higher levels of some other compounds found in coffee, such as antioxidants.
Light roast coffee
Light roast coffee is made from coffee beans that are roasted at a lower temperature for a shorter time. This results in a lighter color and milder flavor than darker roasts. On average, a cup of light roast coffee contains slightly less caffeine than a cup of dark roast, with around 60 milligrams per cup.
Light roast coffee is a good choice for coffee lovers who want to enjoy the taste of coffee without getting too much caffeine. Additionally, light roast coffee is higher in antioxidants than darker roasts, making it a healthy option.
Coffee alternatives
If you want to avoid caffeine altogether, there are several coffee alternatives available. These beverages offer the same rich flavor and aroma as coffee, but they don’t contain any caffeine.
One popular coffee alternative is herbal tea. There are many different types of herbal tea available, including chamomile, peppermint, and ginger. These teas are made by steeping herbs in hot water, and they offer a wide range of health benefits.
Another option is chicory coffee, which is made from roasted chicory root. Chicory coffee has a similar taste and aroma to coffee but doesn’t contain any caffeine. It’s a good choice for people who want to enjoy the taste of coffee without getting a caffeine buzz.
In conclusion, if you’re looking for low caffeine coffee options, there are many alternatives available. From decaf coffee to light roast to coffee alternatives, there are plenty of choices for coffee lovers who want to limit their caffeine intake. Remember to always consult with your doctor if you have any questions or concerns about caffeine consumption.
Health Effects of Caffeine
If you’re a regular coffee drinker, you might be interested to know the health effects of caffeine on your body. In this article, we’ll discuss the positive and negative effects of caffeine, as well as common myths and misconceptions about caffeine.
Positive Effects
Caffeine can have several beneficial effects on the body, including:
– Increased alertness and concentration: Caffeine is a stimulant that can help you feel more awake, alert, and focused.
– Boost in physical performance: Caffeine can improve endurance and reduce fatigue during physical activity.
– Improved mood: Caffeine can stimulate the release of dopamine, a feel-good chemical in the brain, which can enhance mood.
– Reduced risk of certain diseases: Some studies have linked caffeine consumption to a reduced risk of type 2 diabetes, Parkinson’s disease, and liver disease.
Negative Effects
While caffeine can have positive effects, it can also have negative effects if consumed in excess. The negative effects of caffeine can include:
– Anxiety and restlessness: Too much caffeine can cause feelings of anxiousness and restlessness.
– Insomnia: Caffeine can interfere with sleep patterns and cause difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep.
– Digestive issues: Caffeine can irritate the stomach and cause acid reflux, heartburn, and stomach cramps.
– Increased heart rate: Caffeine can have a stimulatory effect on the heart, causing an increase in heart rate and blood pressure.
Myths and Misconceptions
There are many myths and misconceptions about caffeine. Here are a few of the most common:
– Caffeine will dehydrate you: While caffeine is a diuretic (meaning it can increase urine production), it doesn’t cause dehydration unless consumed in very large amounts.
– Caffeine causes cancer: There is no evidence to suggest that caffeine increases the risk of cancer.
– Caffeine is addictive: While caffeine can cause dependence and withdrawal symptoms, it is not considered an addictive substance like drugs or alcohol.
In conclusion, caffeine can have positive effects on the body, such as increased alertness and improved mood, but it can also have negative effects if consumed in excess, such as anxiety and insomnia. Common myths and misconceptions about caffeine include the notion that it causes dehydration and cancer or is an addictive substance. As with any food or drink, moderation is key, and it’s important to be aware of your personal tolerance for caffeine.
Caffeine Intake Recommendations
If you’re wondering how much caffeine is safe to consume, there are standard recommendations for different age groups and populations. Here’s what you need to know:
Safe caffeine intake levels
For healthy adults, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration considers 400 milligrams of caffeine per day (equivalent to about 4 cups of brewed coffee) to be safe. Pregnant women are advised to limit their caffeine intake to 200 milligrams per day (about 2 cups of brewed coffee) to reduce the risk of negative effects on the developing fetus.
Children under the age of 12 should not consume any caffeine, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics, as their bodies are still developing and may be more sensitive to the effects of caffeine.
Individual tolerance
It’s important to note that individual tolerance to caffeine can vary based on several factors, including age, weight, genetics, and overall health. Some people may be more sensitive to caffeine than others and may experience negative effects at lower doses.
To determine your tolerance to caffeine, it’s recommended to start with a low dose and gradually increase over time. Pay attention to how your body reacts to different caffeine sources, whether it be coffee, tea, energy drinks, or other products. If you’re experiencing negative effects such as anxiety, insomnia, or digestive issues, it may be a sign that you need to reduce your caffeine intake or switch to decaf alternatives.
In summary, caffeine intake recommendations vary based on age and health status, with 400 milligrams per day considered safe for healthy adults and 200 milligrams per day recommended for pregnant women. However, individual tolerance to caffeine can vary, and it’s important to listen to your body and adjust your intake accordingly. As always, moderation is key when it comes to consuming caffeine.
How Much Caffeine Do You Need?
If you’re a coffee drinker, you may be wondering how much caffeine you should be consuming to reap the positive effects while avoiding any negative side effects. While the general guideline is up to 400 milligrams (mg) of caffeine a day, the amount that is right for you may vary based on your individual factors and goals.
Factors to consider
There are several factors that can affect how much caffeine you should consume, including:
– Age: Older adults may be more sensitive to the effects of caffeine and may need to consume less.
– Weight: A person’s body weight can impact their caffeine tolerance. Generally, a larger body size can tolerate more caffeine.
– Genetics: Some people may metabolize caffeine more quickly or slowly based on their genetics.
– Other health conditions: Certain health conditions such as high blood pressure or anxiety may require limiting caffeine intake.
Caffeine intake goals
Once you’ve considered your personal factors, you can decide on your caffeine intake goals. Here are some common caffeine intake goals:
– Boosting alertness: Consuming about 50-100 mg of caffeine can provide a boost in alertness and concentration.
– Improving physical performance: Consuming about 100-300 mg of caffeine can improve endurance and reduce fatigue during physical activity.
– Enhancing mood: Consuming about 50-200 mg of caffeine can stimulate the release of dopamine, improving mood.
It’s important to note that everyone’s tolerance for caffeine will be different, and it may take some trial and error to determine what amount works best for you. Additionally, it’s important to consume caffeine in moderation, as excessive caffeine consumption can have negative effects.
In conclusion, determining how much caffeine you need depends on several personal factors, and there are different caffeine intake goals depending on the desired effect. It’s important to be mindful of your personal caffeine tolerance and consume caffeine in moderation.
How Much Caffeine Do You Need?
If you’re a coffee drinker, you may be wondering how much caffeine you need to consume for positive effects while avoiding any negative side effects. Several factors affect caffeine consumption, including age, weight, genetics, and health conditions.
Factors to Consider
When deciding how much caffeine you need, you must consider several factors that can affect caffeine tolerance, such as:
– Age: Older adults may be more sensitive to the effects of caffeine and may need to consume less.
– Weight: Body weight may impact caffeine tolerance, and a larger body size can tolerate more caffeine.
– Genetics: Some people metabolize caffeine more quickly or slowly based on their genetics.
– Health conditions: Certain health conditions such as high blood pressure or anxiety may require limiting caffeine intake.
Caffeine Intake Goals
After considering personal factors, different goals may require varying caffeine intake, including:
– Boosting alertness: Consuming approximately 50-100 mg of caffeine can provide a boost in alertness and concentration.
– Improving physical performance: Consuming about 100-300 mg of caffeine can improve endurance and reduce fatigue during physical activity.
– Enhancing mood: Consuming about 50-200 mg of caffeine can stimulate the release of dopamine, improving mood.
It’s essential to note that everyone’s tolerance for caffeine will differ and may take trial and error to determine the optimal amount of caffeine. Additionally, excessive caffeine consumption can have negative effects making it important to consume caffeine in moderation.
Summary of Caffeine Content in Coffee
A moderate amount of coffee is generally defined as 3-5 cups a day or on average 400 mg of caffeine, according to the Dietary Guidelines for Americans. One 8-ounce cup of brewed coffee contains about 95 mg of caffeine.
Final Thoughts on Caffeine Consumption
Caffeine is a very potent yet unrecognized drug. Although there are positive side effects to caffeine intake, the negative effects can be harmful. Determining how much caffeine you require depends on personal factors, and there are varying caffeine intake goals depending on the desired effect. It’s vital to be mindful of your caffeine tolerance and consume caffeine in moderation.
Conclusion
Knowing how much caffeine you require can provide various benefits, such as boosting alertness, improving physical performance, and enhancing mood. Several personal factors influence caffeine tolerance, and there are differing caffeine intake goals depending on the desired effect. It’s crucial to consume caffeine in moderation, and excessive caffeine consumption can harm the body. Ultimately, finding the right amount of caffeine intake depends on personal circumstances and requires an individualized approach.